Bee stings can be painful and sometimes even cause severe allergic reactions. Knowing how to treat bee stings promptly can alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. In this article of Trendbbq.com, we’ll explore various methods to provide relief from bee stings and offer valuable insights into managing this common outdoor encounter.
Table of Contents,
1. Harm of being stung by a bee
Being stung by a bee can cause varying degrees of discomfort and, in some cases, more severe reactions. Here are some potential effects and risks of bee stings:
- Localized Pain and Swelling: The most common immediate reaction to a bee sting is pain, swelling, and redness at the sting site. This is a normal response to the venom injected by the bee.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to bee stings. Mild allergic reactions can include increased swelling, redness, and itching around the sting site. More severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis, can cause symptoms like difficulty breathing, hives, swelling of the face or throat, rapid pulse, and a drop in blood pressure. Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
- Multiple Stings: If a person is stung by multiple bees, they may experience a higher dose of venom, which can lead to more pronounced symptoms and a greater risk of allergic reactions.
- Bee Venom Allergy Sensitization: Some individuals who are stung by a bee for the first time might develop an allergy to bee venom after the initial exposure. Subsequent stings could then trigger more severe allergic reactions.
- Local Infections: If the sting site is not kept clean and becomes infected, it can lead to additional complications and require medical treatment.
- Stinger Left Behind: Honeybees and some other bees leave behind their stinger along with a venom sac after stinging. It’s important to remove the stinger promptly to reduce the amount of venom injected into the skin.
- Severity Depends on the Person: Reactions to bee stings can vary widely from person to person. Some people might experience only mild discomfort, while others could have more severe reactions.
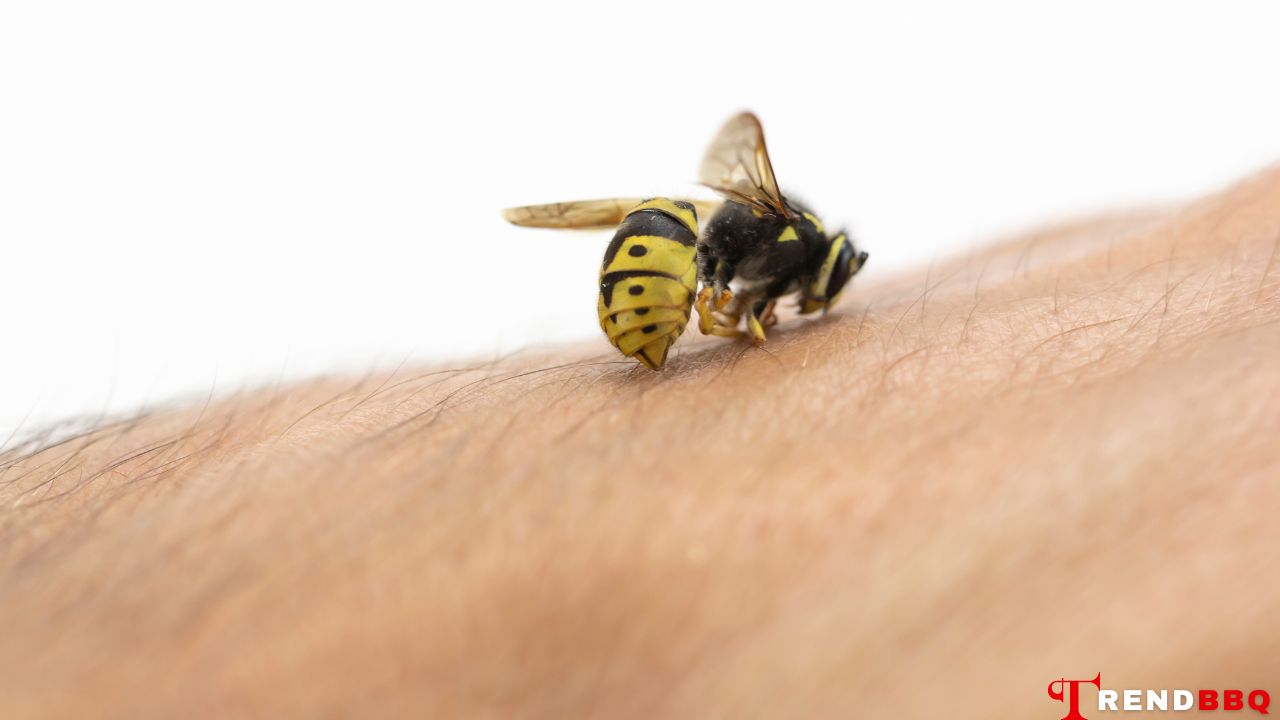

2. Quick First Aid Steps for Bee Stings
- Remove the Stinger: If a stinger is present, gently scrape it off using a flat-edged object, like a credit card. Avoid using tweezers, as squeezing the stinger could release more venom.
- Wash the Area: Clean the sting site with soap and water to help prevent infection.
3. How to treat bee stings
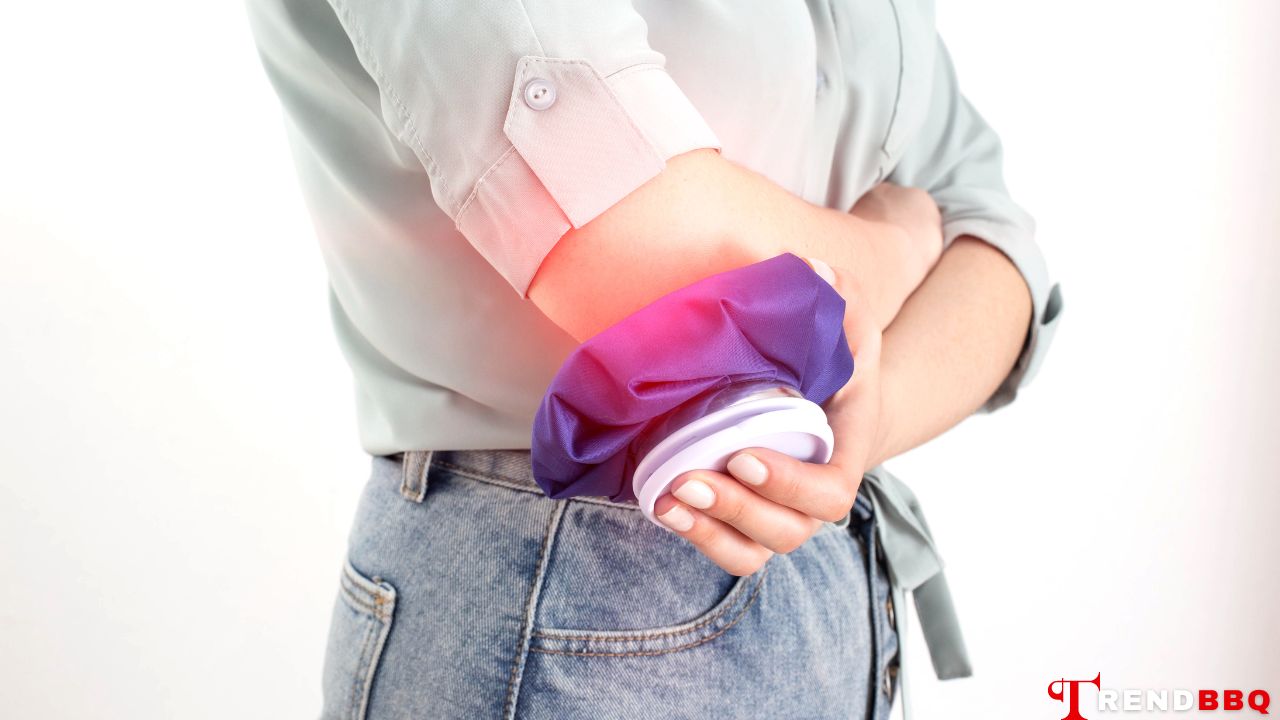
- Cold Compress: Apply a cold compress or ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the sting area. This helps reduce pain and swelling.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Topical Creams: Applying hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to the sting site can help reduce itching and inflammation.
- Natural Remedies: Aloe vera gel, honey, and diluted vinegar solutions can have soothing effects on the sting site.

4. Monitoring for Allergic Reactions
It’s essential to monitor the sting site for signs of an allergic reaction. If you experience difficulty breathing, hives, swelling beyond the sting site, or dizziness, seek medical attention immediately. Individuals with a history of severe allergies or anaphylaxis should always carry an epinephrine auto-injector.
Knowing how to treat bee stings effectively empowers you to handle these minor yet painful encounters with confidence. By promptly removing the stinger, practicing good first aid, and utilizing various treatment methods, you can minimize discomfort and reduce the risk of complications. Remember that while most bee stings cause temporary discomfort, individuals with allergies should take extra precautions and seek medical attention if necessary. By following these guidelines, you’ll be well-prepared to manage bee stings and enjoy the outdoors with greater peace of mind.
5. FAQs
What’s the first thing I should do if I’m stung by a bee?
The first step is to remove the stinger promptly. Use a flat-edged object like a credit card or your fingernail to gently scrape it out. Avoid squeezing or pinching the stinger, as it could release more venom.
How can I relieve the pain and swelling from a bee sting?
After removing the stinger, clean the area with soap and water. Applying a cold compress or ice wrapped in a cloth for 10-15 minutes can help reduce pain and swelling.
Are there any home remedies for bee stings?
Yes, you can try using a paste of baking soda and water or a mixture of meat tenderizer and water on the affected area to help alleviate discomfort. Aloe vera gel and over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream may also help with itching and inflammation.
Can I take an antihistamine for a bee sting?
Yes, taking an over-the-counter antihistamine like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can help reduce itching and allergic reactions. Follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if you’re unsure or experience severe symptoms.
>>> See more: Unlock the Secret: How to Make Rice Water for Hair Growth